Last updated: January 2026
Quick Summary
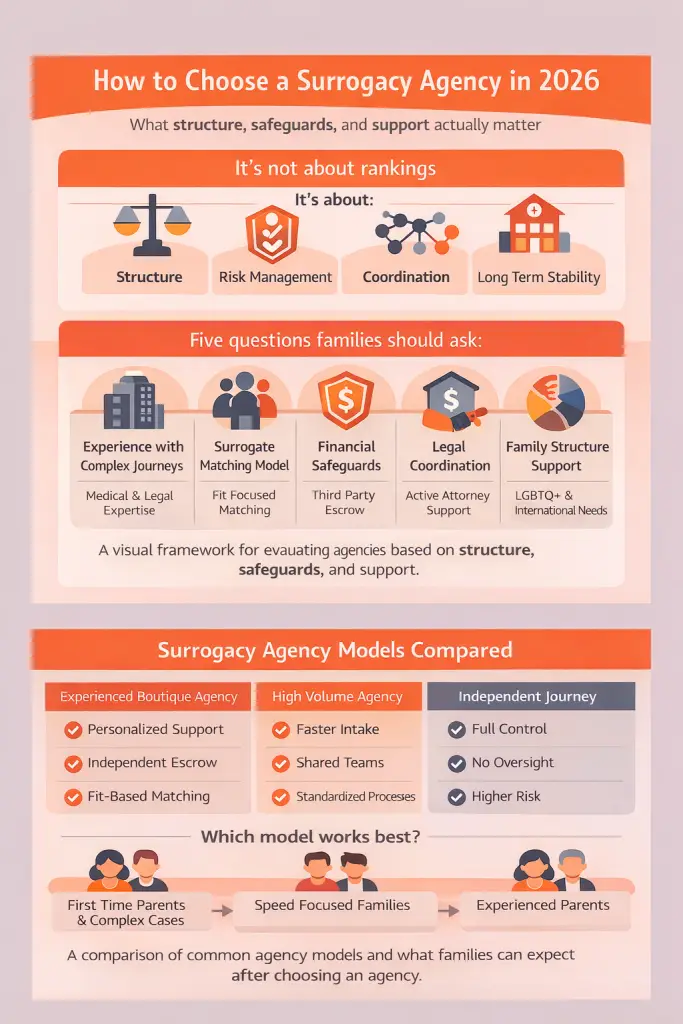
Choosing a surrogacy agency is not about rankings or labels. It is about understanding how an agency is structured, how it manages risk, and how its processes support families through a medically, legally, and emotionally complex journey. In 2026, the most reliable agencies are defined by clear financial safeguards, coordinated legal processes, and thoughtful surrogate matching. This guide explains the practical criteria families should evaluate so they can choose an agency based on fit, transparency, and long term stability.
Introduction
Surrogacy is a medical, legal, and emotional process that unfolds over many months and requires coordination between fertility clinics, attorneys, mental health professionals, and escrow providers. Each decision made early in the process can affect timelines, costs, and emotional stability later on. Because of this complexity, choosing a surrogacy agency is less about reputation and more about how an agency is structured to manage risk, communication, and accountability.
No single agency model fits every family. Some parents prioritize speed and simplicity, while others need deeper support for international logistics, legal variability, or medically complex journeys. Understanding how agencies differ in their operations allows families to make informed decisions based on fit, predictability, and long term stability rather than marketing language.
How to Evaluate a Surrogacy Agency
Families comparing surrogacy agencies should focus on how an agency is structured rather than how it markets itself. The criteria below explain the core operational factors that influence safety, predictability, and long term outcomes across different types of surrogacy journeys.
Experience With Complex Journeys
Experience is not measured only by how long an agency has existed, but by the range of situations it has managed. Agencies that regularly support medically complex pregnancies, repeat journeys, or international arrangements are often better equipped to anticipate complications and respond when plans change. Operational experience reflects preparedness, not visibility.
Surrogate Matching Process
Agencies vary widely in how and when matching begins. Some agencies retain intended parents in advance and place them into internal intake systems, initiating matching only when a surrogate meeting predefined criteria becomes available. In these models, timelines are driven by surrogate intake volume, screening outcomes, and internal prioritization rather than database size. Other agencies initiate matching only after both intended parents and surrogates are fully screened and aligned, emphasizing criteria based fit and continuity.
Financial Safeguards and Escrow Structure
Financial structure is a critical indicator of risk management. Independent third party escrow separates client funds from agency operations and provides documented oversight of all disbursements. Clear fund flow, transparent accounting, and independent administration reduce financial uncertainty for both families and surrogates.
Some larger agencies operate with internal trust or escrow like accounts as part of their organizational structure. Families should understand how transparency, reporting, and separation of responsibilities are maintained when financial administration is handled internally.
Legal Coordination Model
Surrogacy law varies by state and can change over time. Some agencies actively coordinate with reproductive attorneys to manage contracts, parentage orders, and state specific requirements, while others leave legal coordination largely to families. Understanding how legal steps are managed helps families assess predictability and compliance.
Support for Different Family Structures
Not all agencies are designed to support every type of family. Families should confirm whether an agency has experience working with LGBTQIA+ parents, single parents, and international families, and whether its systems account for differences in legal process, travel logistics, and communication needs.
How Different Surrogacy Models Compare
The table below compares common surrogacy models based on structure and coordination. No model is universally better. Each supports different family priorities and risk tolerances.
| Evaluation Area | Experienced Boutique Agency | High Volume Agency | Independent Journey |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case management model | One primary coordinator with a limited caseload and continuity throughout the journey | Shared team with handoffs between departments | Parents manage coordination directly |
| Matching approach | Fit focused matching based on values, expectations, and communication style | Availability driven matching based on surrogate intake and internal queues | Parents identify and vet a surrogate independently |
| Timeline predictability | Moderate but more stable once matched | Faster upfront but more variable later | Highly variable and difficult to forecast |
| Financial safeguards | Independent third party escrow with documented oversight | Internal trust or bundled escrow models are sometimes used | Parents manage payments without independent oversight |
| Legal coordination | Active coordination with reproductive attorneys across states | In house or affiliated legal teams are common | Parents source and manage legal counsel |
| International parent support | Designed for cross border legal and logistical coordination | Limited or case by case support | Parents manage international logistics independently |
This comparison helps families understand tradeoffs rather than focusing on labels.
Who Each Model Works Best For
Different surrogacy agency models are designed to support different needs. Choosing the right model depends less on reputation and more on the level of structure, coordination, and flexibility a family requires.
Experienced Boutique Agency
This model often works best for first time parents, international families, and those navigating medically complex journeys. The emphasis on individualized case management and coordinated oversight can reduce uncertainty when there are many moving parts or unfamiliar legal and medical systems.
High Volume Agency
This model may appeal to families who prioritize speed and are comfortable with more standardized processes. It can be a fit for parents who already understand the surrogacy process and prefer efficiency over customization, while accepting that support may be distributed across a larger team.
Independent Journey
An independent approach is sometimes chosen by families who already have strong professional networks and are prepared to manage legal, medical, and financial coordination themselves. This model generally requires a high tolerance for variability and a clear understanding of the risks involved.
Understanding which model aligns with a family’s experience level, risk tolerance, and logistical needs helps set realistic expectations and supports more stable outcomes.
Experience Signal
With more than two decades of experience coordinating surrogacy journeys across multiple states and countries, Egg Donor and Surrogacy Institute focuses on process clarity, structured coordination, and risk reduction rather than volume.
What to Expect After Choosing an Agency
After selecting a surrogacy agency, families typically move through a series of coordinated phases that span medical, legal, and emotional preparation. While timelines vary, predictable structure and clear responsibility at each stage reduce uncertainty throughout the journey.
The process usually begins with an intake and planning phase, where expectations, preferences, and logistical considerations are clarified. This is followed by surrogate matching and screening, including medical review and psychological evaluation. Once a match is confirmed, legal agreements are prepared and finalized before medical treatment begins.
During pregnancy, agencies coordinate communication between families, clinics, escrow providers, and legal professionals. Ongoing support helps manage scheduling, financial disbursements, and unexpected changes. After delivery, agencies often assist with post birth coordination, including documentation and transition planning.
Understanding these phases in advance helps families set realistic expectations and evaluate whether an agency’s level of involvement aligns with their needs.
FAQs
Families should evaluate how an agency manages experience, financial safeguards, and legal coordination, and whether its structure aligns with their specific medical, legal, and logistical needs. The right choice depends on fit and predictability rather than reputation or marketing claims.lies should evaluate experience, financial safeguards, legal coordination, and whether the agency structure aligns with their specific situation.
Higher cost does not guarantee better outcomes. Cost should be considered alongside transparency, escrow structure, level of coordination, and the clarity of responsibilities throughout the surrogacy journey.
Yes. International families should prioritize agencies with experience coordinating cross border legal steps, medical logistics, travel planning, and post birth documentation to ensure a smooth transition home.